
30 May FITT B-Active beats the corrosive action of chlorine
Chlorine is a fundamental element for the purification of swimming pools and whirlpools. However, it is also highly corrosive: together with the oxidation of water and the thermal-oxidative action of heat, it causes deterioration of hose surfaces.
Resistance to chlorine is therefore one of the main features required in swimming pool hoses.
For this reason, the FITT research and development lab has carried out trials in which it recreated an extreme environment, with the idea of testing the performance levels of FITT B-Active and other hoses found on the market. The hose surface was put into contact with a saturated solution obtained by dissolving trichloroisocyanuric acid normally used in swimming pool skimmers, and bringing the liquid to a temperature of 60 °C.
As it can be seen in the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analysis carried out by the University of Padua, the surface of FITT B-Active remained unchanged, while standard swimming pool hoses, without the original CDS technology, suffered chemical attacks that caused surface corrosion and bubbling effects

FITT B-Active – not corroded surface
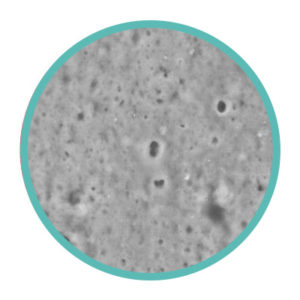
Competitor hose – corroded surface
These defects can become very dangerous, as they cause breaks in the hoses at non accessible points, which in addition to making the swimming pool unusable, also entail significant repair costs.
With its internal surface coated by a patented film resistant to high chlorine contents (Chlorine Defence System, CDS), FITT B-Active can fight chemical attacks from sanitizing products, and therefore can be installed in the direct proximity of the skimmer, which is where the highest chlorine concentration can be measured.





